AWS Velocity Series: Serverless app
The API Gateway provides an HTTPS endpoint that invokes a Lambda function when a request arrives.
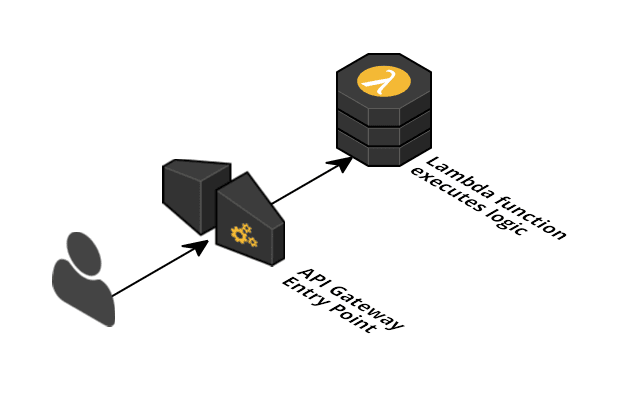
The diagram was created with Cloudcraft - Visualize your cloud architecture like a pro.
As you can see, there is not much infrastructure to set up. To makes things even simpler, you will use the AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM) to reduce the lines of your CloudFormation template to a minimum. All CloudFormation resource types that start with AWS::Serverless:: are transformed by SAM.
AWS Velocity Series
Most of our clients use AWS to reduce time-to-market following an agile approach. But AWS is only one part of the solution. In this article series, I show you how we help our clients to improve velocity: the time from idea to production. Discover all posts!
Let’s start to describe the needed infrastructure.
Serverless app infrastructure
The serverless app infrastructure for the factorial app consists of two parts:
- API Gateway: Provides a configurable HTTPS REST Endpoint that can trigger integrations such as Lambda when a request arrives.
- Lambda function: Lambda provides a fully managed (aka Serverless) runtime for Node.js, Java, Python, and C# code. You upload your code and Lambda runs the code for you.
I will start with the Lambda function.
Lambda function
You can follow step by step or get the full source code here: https://github.com/widdix/aws-velocity
Create a file infrastructure/serverless.yml and describe the Lambda function that is invoked on GET /{number} requests.
|
Lambda dictates an interface that you have to follow. So far, the factorial app is based on express and comes with its own web server. This is no longer needed. Instead, we can have a simpler entry point into the application. Create a file app/handler.js with the following content.
; |
But how do you get notified if something goes wrong? Let’s add a parameter to the Parameters section to make the receiver configurable:
AdminEmail: |
Alerts are triggered by a CloudWatch Alarm which can send an alert to an SNS topic. You can subscribe to this topic via an email address to receive the alerts. Let’s create an SNS topic and two alarms in the Resources section:
# A SNS topic is used to send alerts via Email to the value of the AdminEmail parameter |
Let’s recap what you implemented: A Lambda function that is connected to an API Gateway for GET /{number} requests. In the case of errors, you will receive an Email. All Lambda functions automatically save their logs in CloudWatch Logs.
Now, you can improve the API Gateway setup and add input validation.
API Gateway
An implicit API Gateway is created and configured automatically when using SAM. But if you want to validate the input on the API Gateway, you have to define the API Gateway explicitly to add the API specification in more details by using the open standard Swagger / OpenAPI Spec. Let’s do this in the Resources section:
ApiGateway: |
If you are familiar with Swagger / OpenApi Spec you will find nothing special besides the x-* parameters which are API Gateway specific. You can also monitor the API Gateway. To do so, append the following section the Resources section of your template:
ApiGateway5XXErrorAlarm: |
You will now receive alerts via email if the API Gateway returns an 5XX HTTP status code. API Gateway can also save logs to CloudWatch Logs but SAM lacks support to enable logging at the moment.
Let’s add some outputs to the stack to make it easier to connect with the API Gateway later on.
# A CloudFormation stack can return information that is needed by other stacks or scripts. |
Now you have a production ready Serverless infrastructure defined in CloudFormation with the help of SAM. It’s time to deploy the Serverless app.
Serverless app CI/CD pipeline
The pipeline is based on the CI/CD Pipeline as Code part of this series. The pipeline so far stops when the application artifact (Zip file) is created. An acceptance test artifact is also created. What is missing?
- Create or update an acceptance environment based on the CloudFormation+SAM template
serverless.yml - Run the acceptance tests
- Create or update a production environment based on the CloudFormation+SAM template
serverless.yml
This is how the pipeline looks from the beginning to the end:
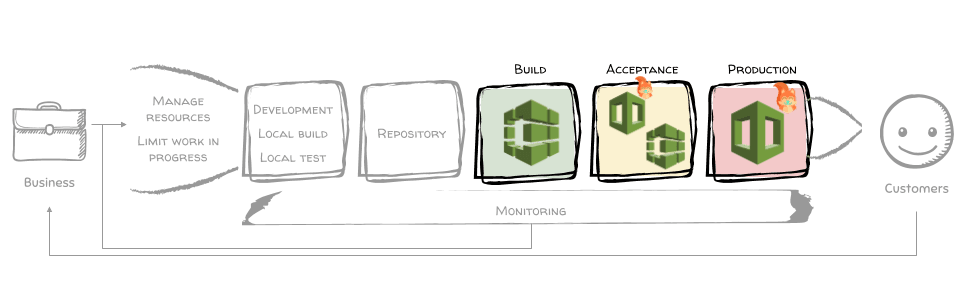
In the EC2 and ECS examples, I used CREATE_UPDATE in the CodePipeline to create or update the CloudFormation stack. At this point, SAM works only if you use CloudFormation Change Sets. Therefore I have to switch from a single CREATE_UPDATE step to CreateChangeSet and ApplyChangeSet in this example.
Copy the deploy/pipeline.yml file to deploy/pipeline_serverless.yml to get the starting point right. If you don’t have the deploy/pipeline.yml file you can download it from https://github.com/widdix/aws-velocity.
Acceptance stage
The acceptance stage consists of a CloudFormation stack based on infrastructure/serverless.yml and the execution of the acceptance tests. To create the CloudFormation stack, you first have to provide a few parameters. Create a file infrastructure/serverless.json with the following content:
{ |
Make sure to change the value of the AdminEmail parameter. Look at the S3Bucket and S3Key parameter value. This is the way of getting the artifact location in CodePipeline.
To run the acceptance tests, you need another CodeBuild project, add the following resources to the Resources section of deploy/pipeline_serverless.yml:
RunAcceptanceCodeBuildRole: |
Now the CodeBuild project needs to be called in the pipeline, therefore change Pipeline resource in the file deploy/pipeline_serverless.yml to:
- deploy the CloudFormation stack suffixed with
-acceptance - run the acceptance tests
Pipeline: |
The acceptance stage is now ready.
Production stage
The production stage is pretty simple, just one CloudFormation stack. Change the Pipeline resource in the file deploy/pipeline_serverless.yml to add a new stage that looks familiar to the acceptance stage:
Pipeline: |
Now the application is deployed to production with confidence and without disturbing the users. Try it and run the pipeline!
Summary
Let’s use my production-ready definition to summarize how each point is implemented:
- Highly available: API Gateway and Lambda are both highly available services out of the box. So your solution is HA as well.
- Scalable: API Gateway and Lambda are both scaled automatically by AWS for you. You have not to manage anything here!
- Frictionless deployment: The new zip file created by CodeBuild is deployed with CloudFormation by changing the value of the parameter which is passed down to the Lambda resource.
- Secure: HTTPS by default. AWS cares about patching. You only need to care about the IAM permissions of your Lambda function. In this case is has only the default permissions to write to CloudWatch Logs.
- Operations: All logs are stored in CloudWatch Logs, important metrics are monitored, and alarms are defined.
If you now have the impression that deploying and running a Serverless app is easy you are right.
Series

- Set the assembly line up
- Local development environment
- CI/CD Pipeline as Code
- Running your application
- EC2 based app
a. Infrastructure
b. CI/CD Pipeline - Containerized ECS based app
a. Infrastructure
b. CI/CD Pipeline - Serverless app (you are here)
- Summary
You can find the source code on GitHub.
