How to analyze and reduce S3 storage usage?
S3 is an object store, not a file system. Object storage comes with significant advantages: unlimited storage capacity, high availability, and durability. However, there are some disadvantages too. For example, it is cumbersome to calculate the storage usage of a specific prefix (also known as a folder) in S3.

For example, I’m using an S3 bucket to store personal data.
|- backups/ |
The CloudWatch metric BucketSizeBytes shows the storage usage of each S3 bucket broken down by storage class. Currently, it takes about 460 GB to store my data. That’s $5.60 per month.
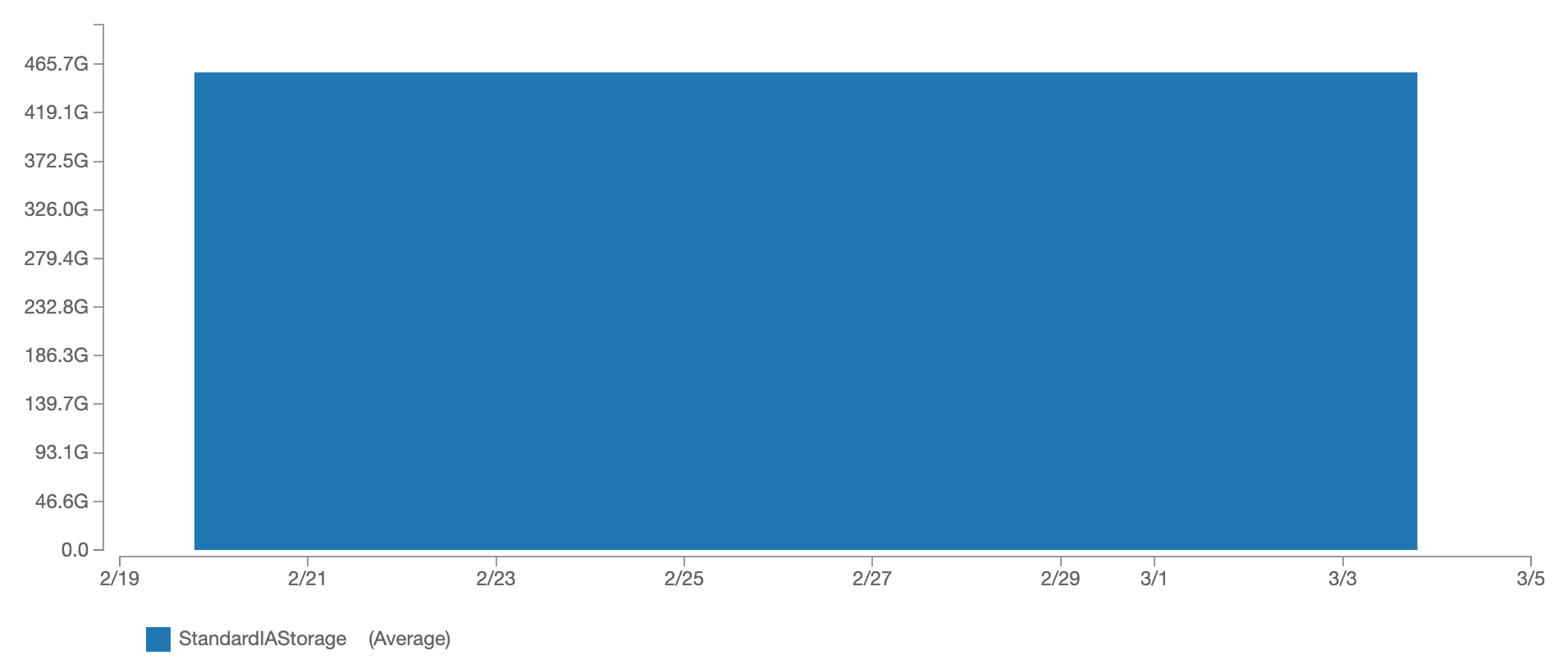
To reduce costs, I’d like to delete unused data. But where to start looking for data that is no longer valuable to me? My bucket contains more than 100,000 objects. Therefore, I want to find the prefixes (also known as a folder) with the highest storage consumption.
Doing so isn’t easy. Neither the AWS Management Console nor the S3 API provides a way to fetch the storage usage per prefix. Remember, S3 is an object store, not a file system. In theory, you could list all objects in the bucket, retrieve the object size, and calculate the storage usage per prefix on your own. But doing so is cumbersome, slow, and costly.
Luckily, there is a better way to analyze S3 storage usage.
- S3 Inventory provides CSV, ORC, or Parquet files listing all the objects stored within an S3 bucket on a daily or weekly basis.
- Athena queries CSV, ORC, or Parquet files and analyzes data on-the-fly.
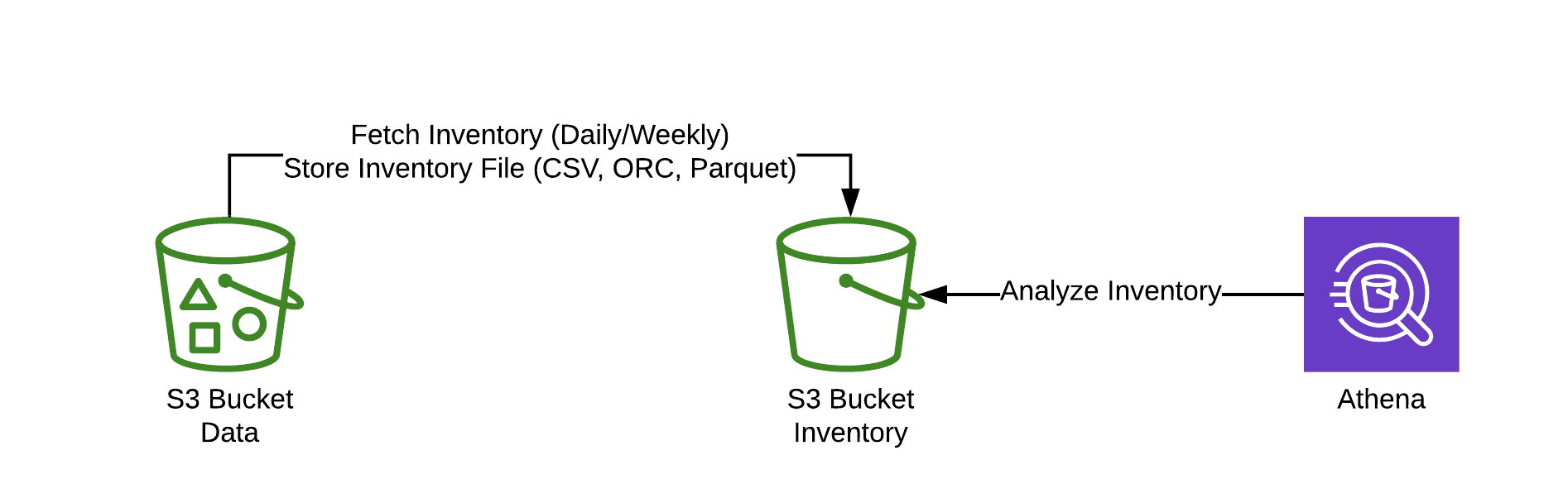
Next, you will learn how to enable S3 Inventory, set up Athena, and analyze storage usage with Athena.
Enabling S3 Inventory
Go through the following steps to enable S3 Inventory for a bucket.
- Open the AWS Management Console.
- Go to Simple Storage Service (S3).
- Create a new bucket to store the inventory files.
- Open the bucket you want to analyze and reduce S3 storage usage.
- Switch to the
Managementtab. - Select
Inventory. - Press the
Add newbutton. - Fill out the details, as shown in the following screenshot.
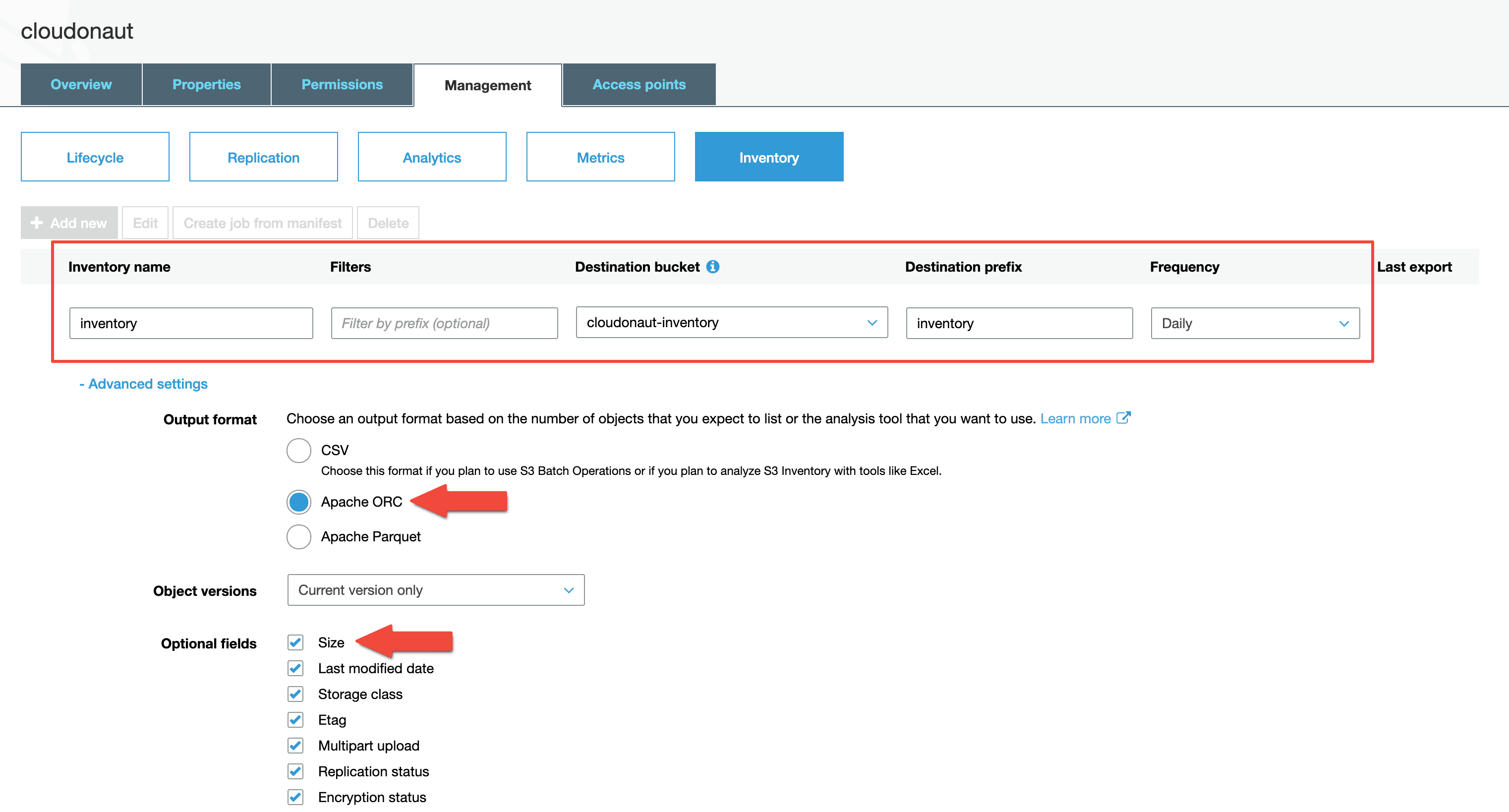
Please note, it will take up to 24 hours until the first inventory files will show up in the inventory bucket.
Setting up Athena
To run SQL queries to analyze the inventory data, you need to create an Athena table first. Go to the Athena service in the AWS Management Console to do so.
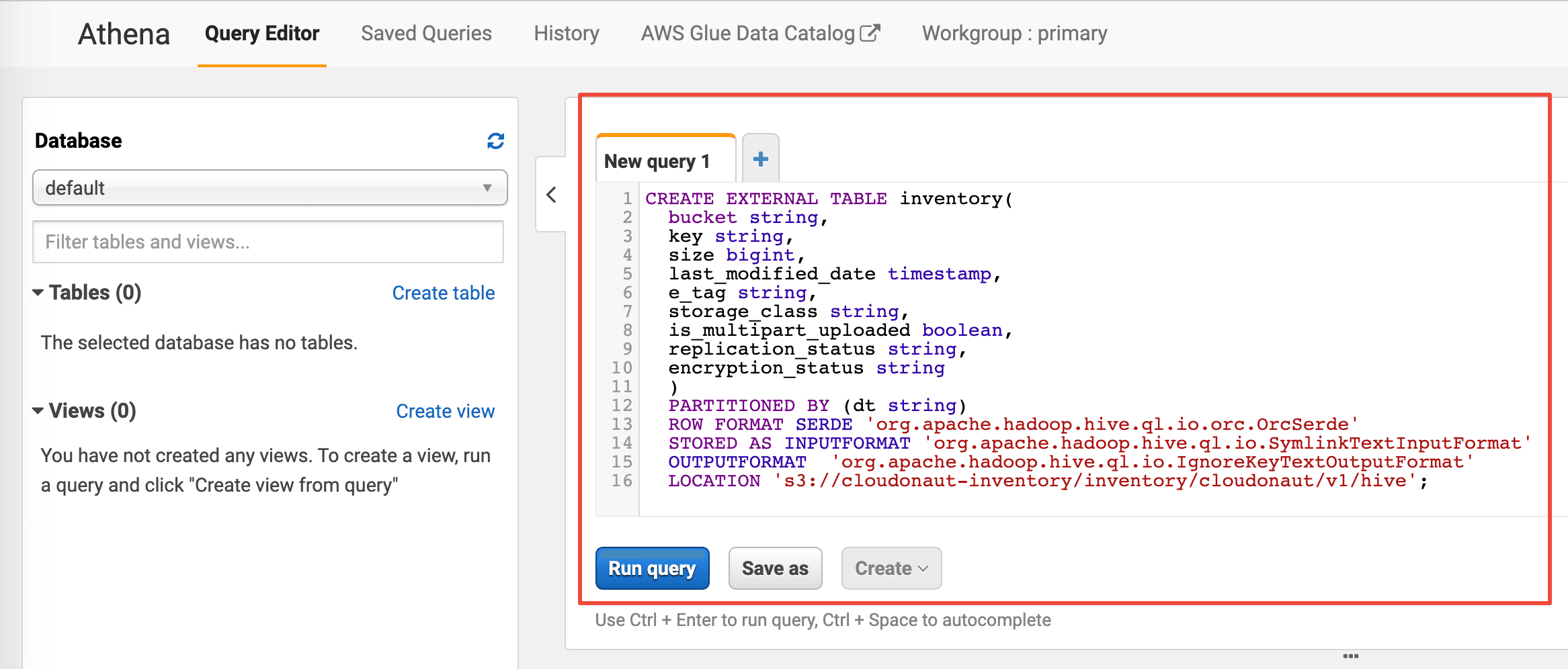
Next, execute the following query to create the inventory table. Replace $InventoryBucket, $InventoryPrefix, $Bucket, and $InventoryName with the configuration from the previous section.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE inventory( |
Also, you need to make sure that the partitions of the table are updated. Do so by executing the following command.
MSCK REPAIR TABLE inventory; |
That’s it; you have configured Athena. You are ready to analyze the inventory data.
Analyzing storage usage with Athena
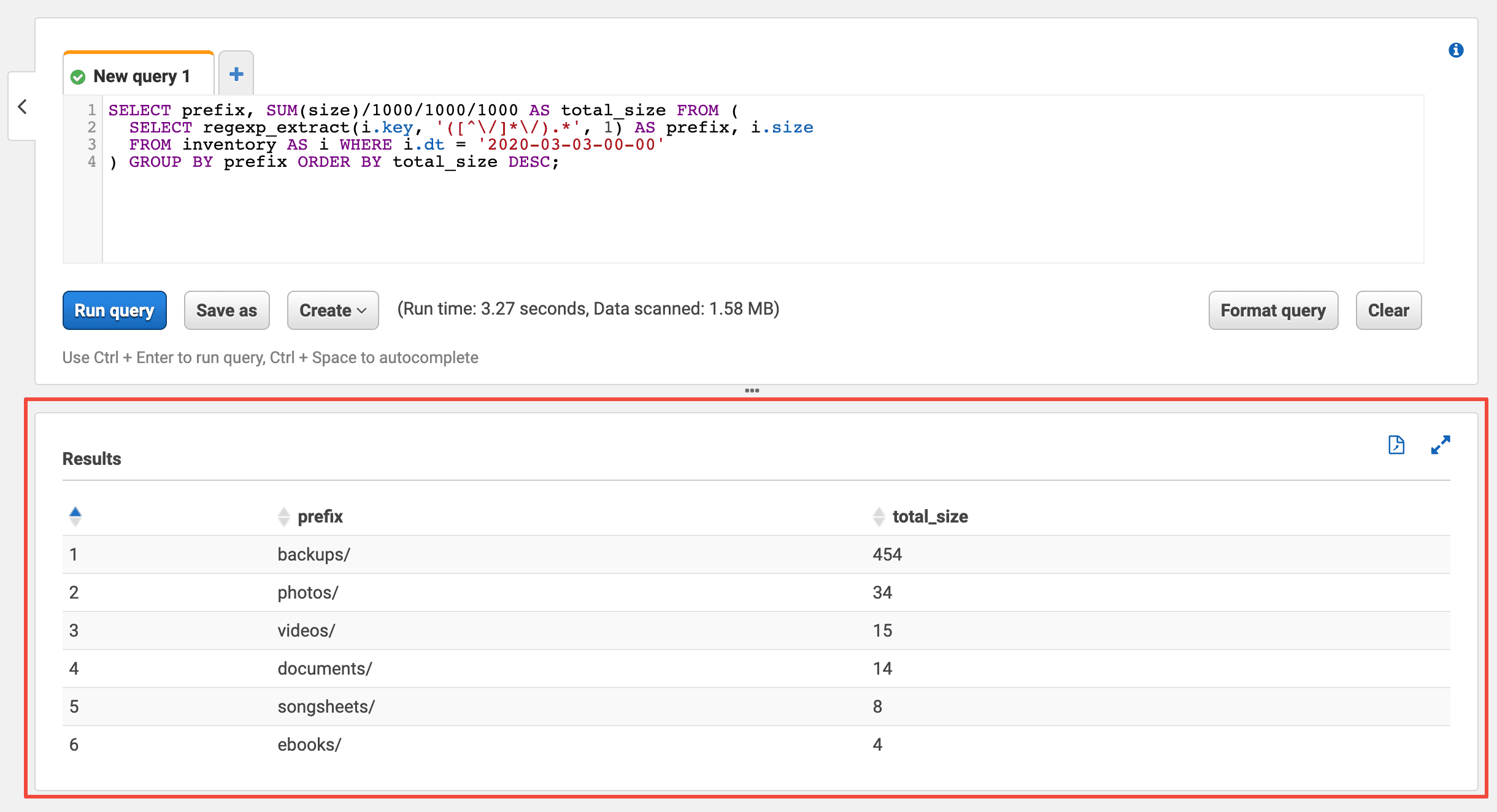
Execute the following query to analyze the storage usage by the first part of the prefix. Replace $Yesterday with yesterday’s timestamp (e.g., 2020-03-03-00-00).
SELECT prefix, SUM(size)/1000/1000/1000 AS total_size FROM ( |
In my case, the objects with prefix backups/ use 454 GB of storage. So I know where to look for data that is no longer valuable to me to reduce storage costs.
Please note, I have used a personal bucket with less than 500 GB as an example in this blog post. However, the shown concept works for buckets with vast amounts of objects and data as well.
