How to create a customized CloudWatch Dashboard with CloudFormation
Which metrics are essential to evaluate the state of your cloud infrastructure? Probably a lot. A dashboard allows you to keep an eye on all these metrics. For example, I like to monitor the following metrics for a typical 3-tier web application with the help of a CloudWatch dashboard:
- load balancer: client-side and server-side error rates
- load balancer: target response latency and number of requests
- compute: CPU and memory utilization
- database: query and I/O throughput

But how to create a customized CloudWatch Dashboard with CloudFormation? Doing so is possible with a simple CloudFormation template. However, I choose to use a custom resource to be more flexible when generating the dashboard. The following steps are needed to create a CloudWatch dashboard with a custom resource.
- Create a CloudFormation template and add a Lambda-backed custom resource.
- Write the code creating, updating, and deleting a CloudWatch dashboard.
- Generate the JSON code describing the customized dashboard.
You will learn how to do so in more detail next.
Create a template and add a Lambda-backed custom resource
First of all, create a CloudFormation template. Add the identifiers of the resource you want to monitor to the parameters section as shown in the following code snippet.
|
Next, you need to add three resources to your template.
- A custom resource
Dashboardto manage the CloudWatch dashboard. - A Lambda function
CustomResourceFunctionexecuting your source code for the custom resource. - An IAM role
CustomResourceRoleassumed by the Lambda function to write logs as well as creating, updating and deleting CloudWatch dashboards.
# ... |
And now we’ll write some code.
Implement creating, updating, and deleting a CloudWatch dashboard
The following code snippet shows parts of dashboard.js including the handler which creates, updates, or deletes a CloudWatch dashboard. The built-in modules aws-sdk and cfn-response are used.
const AWS = require('aws-sdk'); |
There is only one step missing: you need to add widgets to the dashboard.
Generate the JSON code describing the customized dashboard
To do so, you need to generate a JSON file describing your dashboard in Dashboard Body Structure and Syntax
. I recommend to create your dashboard by clicking through the AWS Management Console first. Generating the dashboard’s JSON with the help of the View/edit source action gives you a good starting point.
The following code snippet shows the generateDashboard function, which generates the JSON defining a CloudWatch dashboard with two widgets:
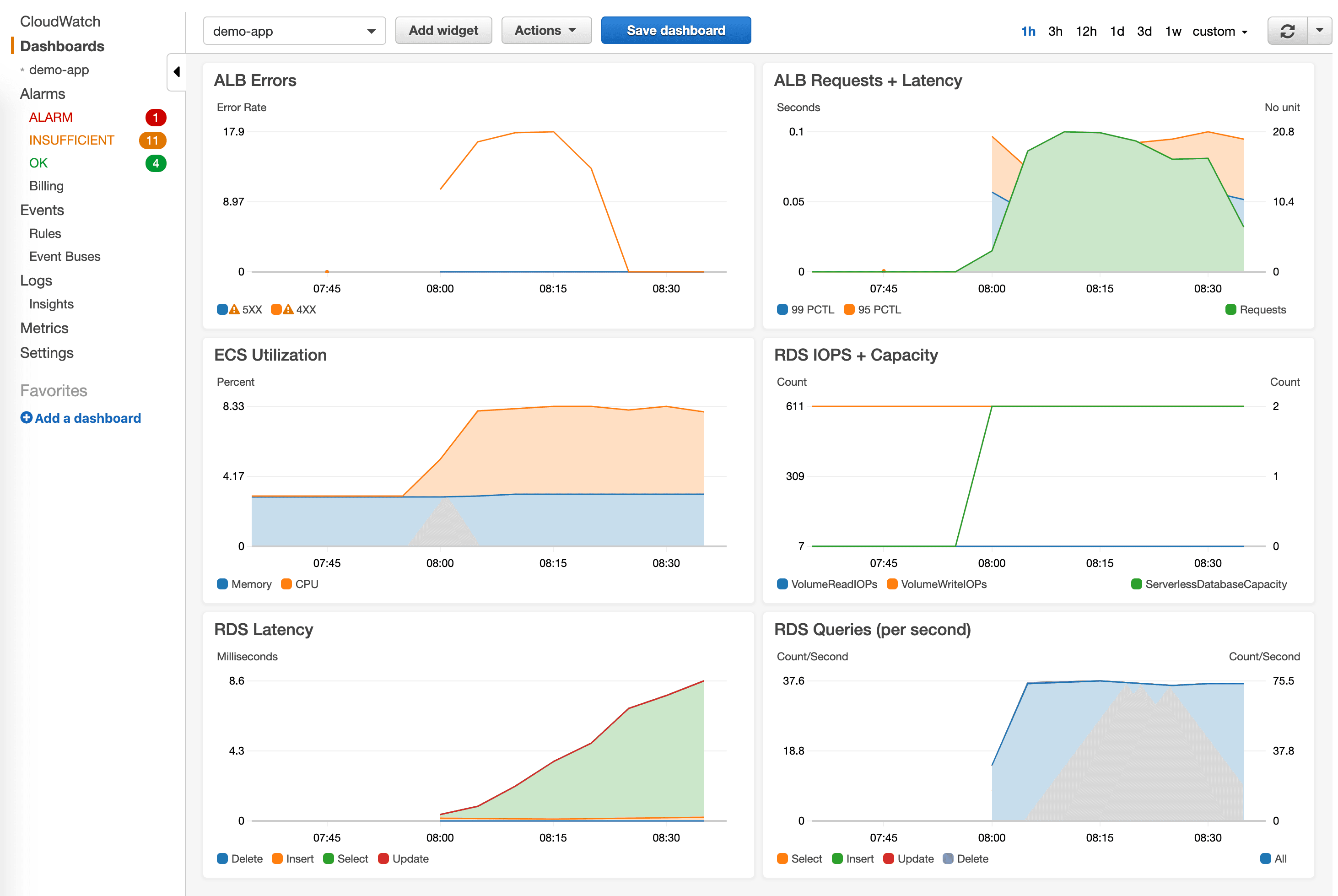
- Widget ALB: total number of incoming requests as well as the target latency in 99 and 95 percentile
- Widget RDS: maximum read and write IOPS as well as the serverless capacity of the database
function generateDashboard(event) { |
That’s it. The following screenshot illustrates the results.
Looking for a more advanced example? Check out the source code of our CloudFormation modulecfn-modules/cloudwatch-dashboard.
Let’s knuckle down! 👩💻
Further reading
- Article Verify SNS messages delivered via HTTP(S) in Node.js
- Article Analyze CloudWatch Logs like a pro
- Article Monitoring EC2 Network Utilization
- Tag cloudformation
- Tag cloudwatch
