Rapid CI/CD with CodeBuild to deploy PHP and Docker
There are many options available when you are looking for ways to implement a deployment pipeline. You might have heard about Jenkins, CircleCi, BitBucket Pipelines, GitLab Pipelines, and many others. AWS, on the other hand, offers services for CI/CD itself: CodeBuild and CodePipeline.

AWS CodePipeline orchestrates deployment pipelines. Unfortunately, the learning curve is steep and the implementation is often complicated. Therefore, I recommend a more simple approach: use CodeBuild. In general, CodeBuild feels like CircleCI or GitLab Pipelines. However, CodePipeline offers tighter security controls and excellent integration into your AWS infrastructure.
Do you prefer listening to a podcast episode over reading a blog post? Here you go!
The following figure demonstrates how a simple CI/CD pipeline built with CodeBuild works.
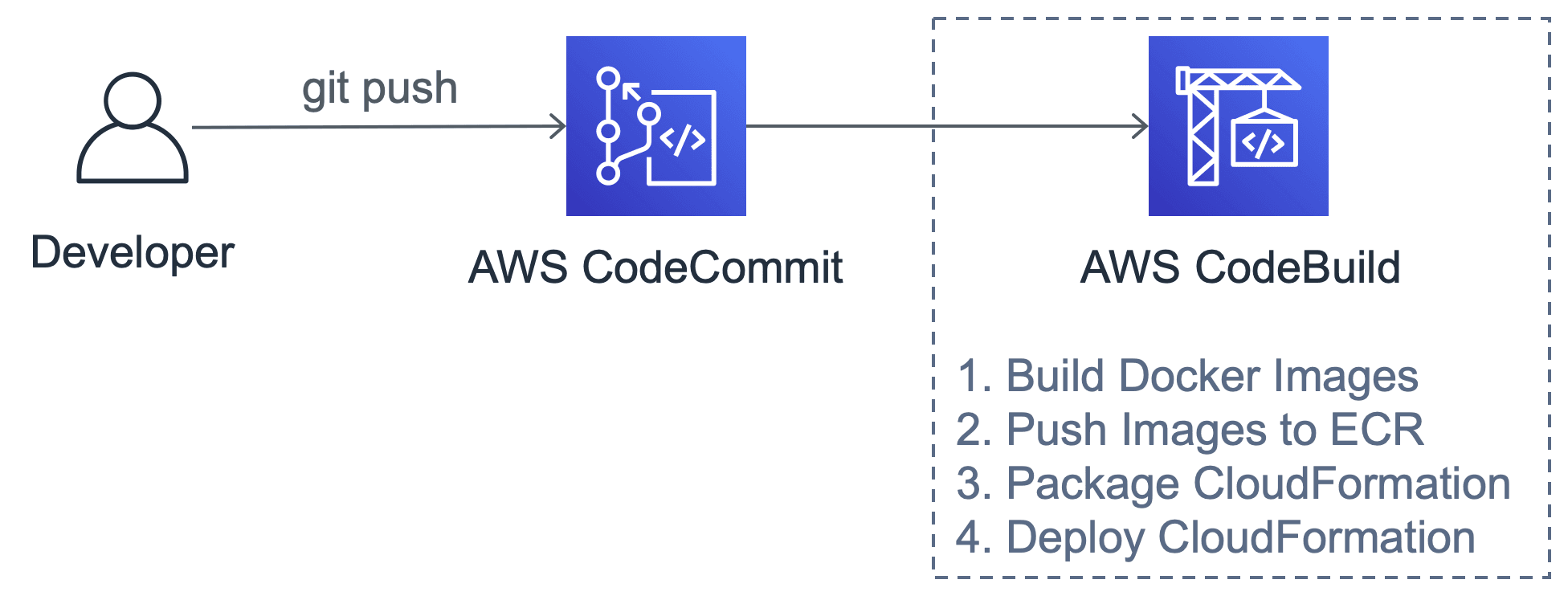
AWS CodeBuild fetches code from CodeCommit and executes commands that you define in a file called buildspec.yml placed in the root directory of your project folder and repository. The following buildspec.yml changes the directory and runs the npm i command.
version: 0.2 |
The version attribute specifies the schema of the buildspec.yml and is defined by AWS. Multiple phases are supported and run in the following order:
installpre_build(ifinstallsucceeded)build(ifpre_buildsucceeded)post_build(ifbuildfailed or succeeded)
Each phase runs a series of commands — defined by you — using the same instance of the default shell (we will use Bash) as the execution environment. Besides the environment variables that CodeBuild provides out of the box, you can also define custom environment variables to keep your buildspec.yml more flexible.
Deployment steps defined in buildspec.yml
The following steps are needed to deploy a dockerized PHP application to an infrastructure managed by CloudFormation based on cfn-modules:
- Build the
nginxDocker image - Build the
php-fpmDocker image - Push both Docker images to ECR
- Install cfn-modules by executing
npm iin theawsfolder - Package the CloudFormation template (
aws cloudformation package) - Deploy the CloudFormation template with the new Docker images (
aws cloudformation deploy)
The following buildspec.yml installs Docker, executes the docker login command returned by aws ecr get-login and finally, runs the Bash script: build.sh. The Bash script is the place for your own customizations and helps us to keep the buildspec.yml clear.
version: 0.2 |
Let’s look at build.sh to see how steps 1-6 are implemented. The build.sh script is invoked by the buildspec.yml with bash build.sh. Therefore, the script lives side-by-side with the buildspec.yml file. The first two lines state that this is a Bash script that ends execution if one of the commands fails.
|
The next lines create the names and tags for the Docker images:
NGINX_NAME_TAG="${ACCOUNT_ID}.dkr.ecr.${REGION}.amazonaws.com/\ |
Next, the script executes docker build to build the two Docker images, followed by docker push to upload the Docker images to ECR. Depending on the web application that you want to dockerize, you might want to add additional commands here (e.g., producing a JAR file, downloading dependencies, running unit tests or static analysis).
docker build -t "${NGINX_NAME_TAG}" \ |
After that, we need to change to the aws directory, which contains the Infrastructure as Code, install the cfn-modules, and package the CloudFormation template:
cd aws |
Finally, the CloudFormation template is deployed and the new Docker images are passed as parameters:
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file .template.yml \ |
Creating a CodeBuild project
So far, we have transformed the manual deployment steps into a repeatable Shell script. Next, you’ll configure CodeBuild to connect the dots. A CodeBuild project fetches code from CodeCommit and executes the commands defined in the buildspec.yml. Whenever you push a new commit to your CodeCommit repository, CodeBuild will start automatically. The following snippet shows how to create a CodeBuild project with CloudFormation. Doing so allows you to use Infrastructure as Code to set up your deployment pipeline. A more detailed explanation will follow.
Resources: |
The important pieces of the CloudFormation snippet are:
- The
Environmentproperty, which defines the custom environment variables that are used to keep thebuildspec.ymlfile more flexible. Add more variables here if you need them in your modifiedbuild.shscript. - The
LogsConfigproperty, which specifies the CloudWatch Logs location where logs are stored that you can use to debug problems with the pipeline. - The
ServiceRoleproperty, which points to the IAM role that is used when executingbuildspec.yml. The role needs permissions to download the source code from CodeCommit, write to CloudWatch Logs, deploy the CloudFormation template, and push images to ECR. If you want to call other AWS services in yourbuild.shscript, you likely need to add additional permissions here.
